[Paper] PointNet: Deep Learning on Point Sets for 3D Classification and Segmentation
Main contribution
- 직접적인 point cloud 처리 point cloud data를 grid로 변환하거나 복잡한 전처리 과정을 거치지 않고 직접 처리 data의 원래 형태를 보존하며 처리 과정에서 발생할 수 있는 정보 손실을 최소화
- 순서 불변성 point의 순서에 의존하지 않음 물체가 회전한다고 해서 다른 물체가 되는것이 아니기 때문에 또한 transform에도 invariant 해야함 이를 위해 네트워크 입력으로 들어오는 모든 point에 대해 독립적으로 feature 추출 max pooling 사용하여 global feature 집계
- segmentation and classification point 별 분류를 통해 객체 내부의 각 점에 레이블을 지정하는 segmentation 작업에도 효과적
Architecture
- feature extraction 각 point에서 local feature를 독립적으로 추출(w MLP)
- feature aggregation 모든 point의 feature를 집계하여 global feature 생성 max pooling 사용
- classification, segmentation network global feature를 사용하여 수행
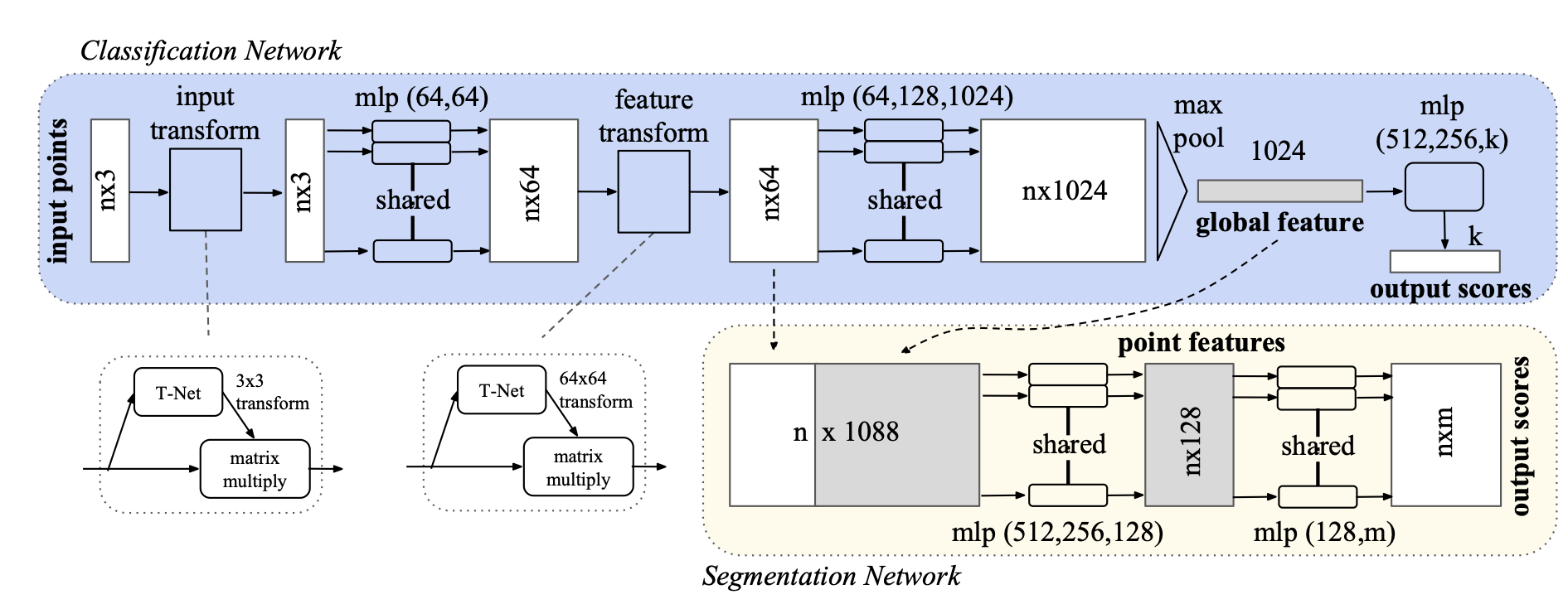
input
- subset of points from euclidean space
- (x,y,z) 채널만 사용
- k: candidate class
- m: semantic sub-categories
아래 3개가 모델의 핵심 내용
input permutation에 대해 invariant하려먼 어떤 방법을 써야하나?
- input을 canonial하게 정렬 고차원 공간에서 point perburtation에 안정적인 order가 존재하지 않는다고 함(?)
- input 을 sequence로 다뤄 모든 permutation에 대해 augment(invariant를 챙기기 위해서는 하나의 sequence에 대해 변형된 모든 sequence에 대해서도 알아야 하니까) N!의 순서들이 생기고 너무 큰 스케일이 된다. 실험했을때도 PointNet보다 결과 안좋았다고 함
- symmetric function 사용 -> 변형된 set 의 element에 maxpooling 사용하여 general function 근사하는게 목표 mlp와 maxpool 사용하여 함수 근사하면 invariant 챙길 수 있다
segmentation의 경우에는 local과 global 정보 모두 필요하기 때문에 입력시 global feature를 각 point 에 합쳐준다
Joint Alignment Network
transformation에 invariant 하기 위한 방법
T-net이라는 미니 네트워크 사용 affine transformation matrix(변환행렬)에 해당하는 network로 이 네트워크를 통과했는데도 semantic label이 그대로 나온다면 invariant 하다고 볼 수 있다
affine transform은 시점에 따라 물체의 생김새가 다른 걸 뜻함 때문에 T-net을 통해 이 변환을 진행하고 이때 생기는 semantic label이 같다면 이는 transformation에 invariant
feature space에서 transformation matrix는 spatial transformation matrix보다 고차원이라서, 최적화의 어려움이 생긴다 때문에 regularization term 추가
